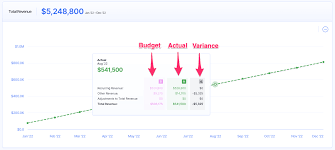
Budgeting is an essential financial practice for businesses, but actual financial performance often deviates from projections. Actual vs. budget variance analysis is a powerful tool that helps organizations assess these differences and make informed decisions. By identifying and understanding variances, businesses can improve financial planning, control costs, and optimize overall performance.
This blog outlines a step-by-step approach to conducting an effective actual vs. budget variance analysis.
Step 1: Gather Financial Data
The first step in variance analysis is to collect accurate financial data. This includes:
- Budgeted financial statements – These documents outline expected revenue, expenses, and profits, forming the baseline for comparison.
- Actual financial data – These include income statements, cash flow statements, and expense reports that detail real financial performance.
- External financial factors – Economic conditions, inflation rates, market trends, and unexpected financial events can influence actual performance.
Ensuring data accuracy is crucial, as any errors could lead to misleading variance results. Utilizing accounting software or financial management tools can help maintain precision and streamline data collection.
Step 2: Calculate Variances
Once the data is gathered, the next step is to compute the variance for each financial metric. This is done using the formula:
Variance = Actual Value – Budgeted Value
- A positive variance means actual results exceeded budget expectations (e.g., higher revenue than planned), which is typically favorable.
- A negative variance means actual results fell short of budgeted projections (e.g., higher expenses than expected), which may indicate financial inefficiencies.
- A zero variance means actual performance matched the budget exactly, reflecting accurate forecasting.
Calculating variances allows businesses to pinpoint areas of concern and opportunities for improvement.
Step 3: Categorize the Variances
After calculating variances, categorizing them helps in understanding their impact and root causes:
- Revenue Variance – The difference between projected and actual income. This could be due to pricing changes, demand fluctuations, or marketing effectiveness.
- Cost Variance – Discrepancies in expenses such as raw materials, labor, or overhead costs. Operational inefficiencies or unexpected price hikes may contribute to this.
- Profit Variance – The difference between budgeted and actual profit margins, influenced by both revenue and cost variances.
By categorizing variances, businesses can identify whether the issue lies in sales performance, cost management, or overall profitability.
Step 4: Identify Root Causes
Analyzing variances requires identifying the underlying reasons behind the differences. Some common causes include:
- Sales fluctuations – Changes in customer demand, competition, or seasonal variations.
- Operational inefficiencies – Delays in production, supply chain disruptions, or increased labor costs.
- Economic factors – Inflation, interest rate changes, or currency exchange fluctuations affecting financial stability.
- Internal errors – Incorrect budget estimates, misallocated funds, or errors in financial reporting.
Understanding these causes allows businesses to take corrective action and refine future budgeting strategies.
Step 5: Interpret Variance Impact
Not all variances are negative. Some indicate opportunities for growth, while others highlight potential risks. Evaluating the significance of each variance helps determine the appropriate response:
- Favorable Variances: If revenue is higher than expected, consider reinvesting profits into business expansion, marketing efforts, or employee incentives.
- Unfavorable Variances: If costs exceed budgeted amounts, assess whether expenses can be controlled through supplier negotiations, efficiency improvements, or cost-cutting measures.
Assessing the impact of variances ensures that businesses make data-driven financial decisions rather than reactive changes.
Step 6: Take Corrective Actions
After identifying and interpreting variances, businesses should implement strategies to address unfavorable variances and leverage favorable ones. Potential actions include:
- Adjusting pricing strategies – Increasing or modifying pricing structures to align with market trends and profitability goals.
- Reducing unnecessary costs – Streamlining operations, renegotiating contracts, or finding alternative suppliers to cut expenses.
- Improving operational efficiency – Automating manual processes, investing in better technology, or training employees to enhance productivity.
- Refining future budgets – Using historical variance data to create more accurate and realistic budgets in the next financial cycle.
Taking proactive measures ensures that financial goals remain achievable and that variances do not negatively impact long-term business success.
Step 7: Monitor and Review Regularly
Variance analysis should be an ongoing process rather than a one-time task. Businesses should:
- Conduct variance analysis periodically – Monthly or quarterly reviews help in identifying trends and making timely adjustments.
- Adjust forecasts dynamically – Revising projections based on real-time financial performance ensures better alignment with market conditions.
- Continuously refine budgeting techniques – Learning from past variances enables organizations to improve budgeting accuracy and financial planning.
Regular monitoring ensures that businesses remain financially agile and can adapt to changing economic and operational conditions.
Conclusion
Conducting an actual vs. budget variance analysis helps businesses maintain financial discipline and adapt to changing conditions. By regularly monitoring variances, identifying root causes, and taking corrective actions, organizations can enhance their financial decision-making and achieve long-term success.
Need expert financial insights? Contact us today to optimize your budget variance analysis!